

Takegawa Y, Seguchi K, Ito S, Yoshioka S, Nakagawa H, Nishimura S. Structural assignment of isomeric 2-aminopyridine-derivatized oligosaccharides using MSn spectral matching. Amino functional group synonyms, Amino functional group pronunciation, Amino functional group translation, English dictionary. Takegawa Y, Ito S, Yoshioka S, Deguchi K, Nakagawa H, Monde K, Nishimura S. Structural characterization of oligosaccharides using MALDI-TOF/TOF tandem mass spectrometry. N-Linked glycosylation in Campylobacter jejuni and its functional transfer into E. Functional groups are chemical motifs, or patterns of atoms, that display. Often, these additional atoms appear in the context of functional groups. Wacker M, Linton D, Hitchen PG, Nita-Lazar M, Haslam SM, North SJ, Panico M, Morris HR, Dell A, Wren BW, Aebi M. Large biological molecules are generally composed of a carbon skeleton (made up of carbon and hydrogen atoms) and some other atoms, including oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur.
However, in these compounds, the carbonyl group is.

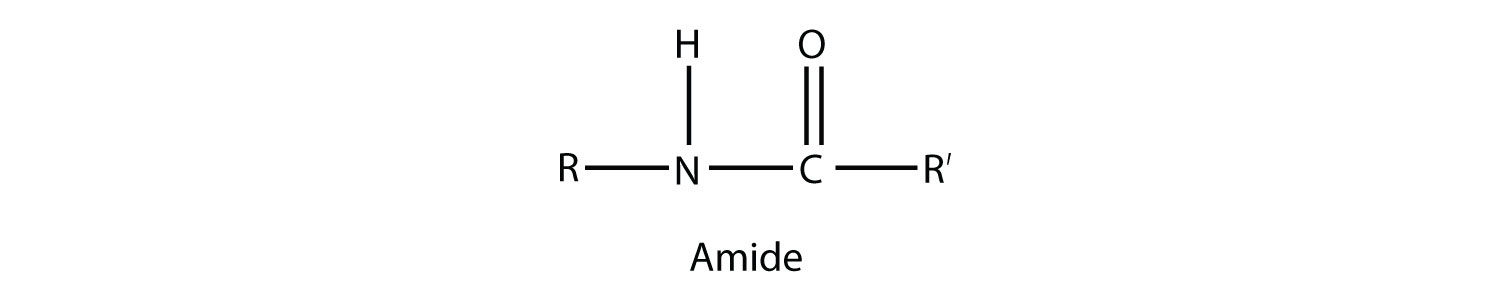
The carbonyl group is also found in carboxylic acids, esters, and amides. We introduced the carbonyl group (CO)the functional group of aldehydes and ketonesin Chapter 14 'Organic Compounds of Oxygen'.
Amino functional group update#
Analysis of carbohydrates and glycoconjugates by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry: an update covering the period 1999–2000. Identify the functional group for a carboxylic acid, an ester, an amine, and an amide. These results are consistent with the fragmentation of lacto-neo-N-tetraose and maltotetraose, suggesting that a sodium cation generally localizes much more frequently on the acetamide group in sugar chains. Thus, their ions with HexNAc are abundant. In contrast, a sodium cation localizes much more frequently on the acetamide group in acetamide-CyDs because the chemical species with HexNAc are stable. Sodium cation (Na(+)) attachment is independent from amino group and exerts no influence on their fragmentation patterns in amino group except for mono- and disaccharide fragment ions because there is the possibility of the reducing end effect. Consequently, the results indicate that a proton (H(+)) localizes on the amino group of the amino sugar, and that the proton (H(+)) induces their fragmentation. Interestingly, the relative ion intensities and isotope-like patterns in their product ion spectra depend on the functional groups and ion forms of sugar chains. CyD derivatives substituted by amino or acetamide groups are ideal analytes to extract the function group effects, which are amino-CyD with one hexosamine (HexNH2) and acetamide-CyD with one N-acetyl hexosamine (HexNAc). To elucidate the influence of amino (-NH2) and acetamide (-NHCOCH3, -NAc) groups in sugar chains on their ionization and fragmentation, cycloamyloses (cyclodextrins, CyDs) and lacto-oligosaccharide are analyzed by MALDI TOF/TOF and ESI Q-TOF mass spectrometry.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
